Cement Production in the last 10 years: Trends and Insights

Cement is a foundational material in construction, playing a pivotal role in infrastructure and urban development worldwide. Over the past decade, global cement production and consumption patterns have evolved significantly, reflecting economic shifts, urbanization trends, and regional growth priorities. This blog delves into cement production trends, key consumption patterns, and per capita usage across major countries to provide insights into the industry’s progress and its impact.
Global Cement Production Trends (2012-2022)
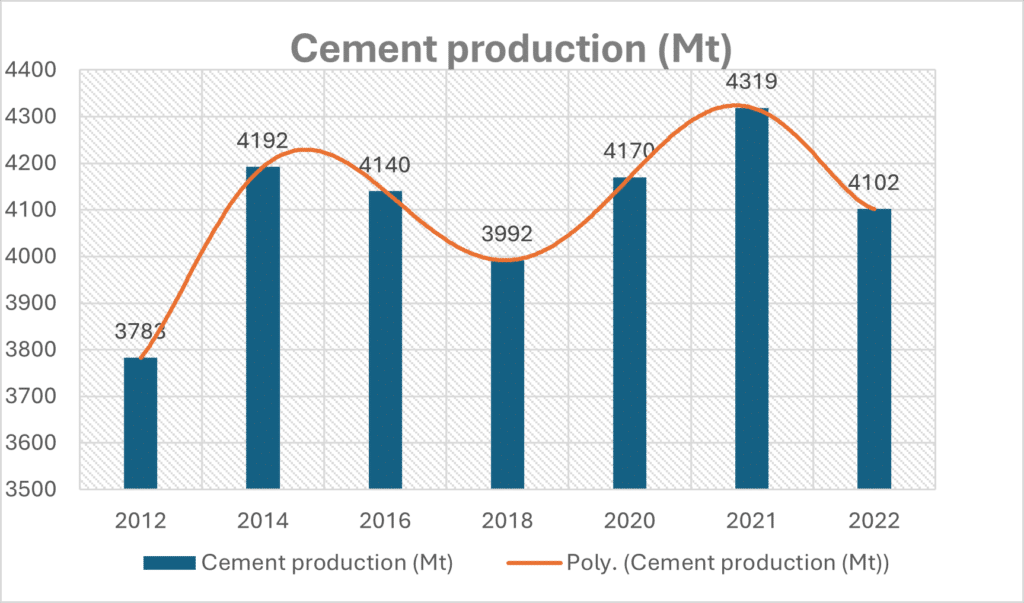
Driven by construction booms in developing economies, the cumulative production average of cement has steadily increased over the years. Infrastructure projects, urbanization, and the growth of affordable housing initiatives have been key contributors to this upward trend. During the COVID-19 pandemic, when most countries were in lockdown and numerous industries faced unprecedented disruptions, the cement industry emerged as an outlier. While global manufacturing sectors experienced significant downturns, cement production demonstrated remarkable resilience. Interestingly, the cement industry achieved its highest production levels to date during this challenging period. Despite the economic slowdown, the continued demand for cement reflects its indispensable nature in both public and private construction projects.
Major Cement-Consuming Countries in 2022
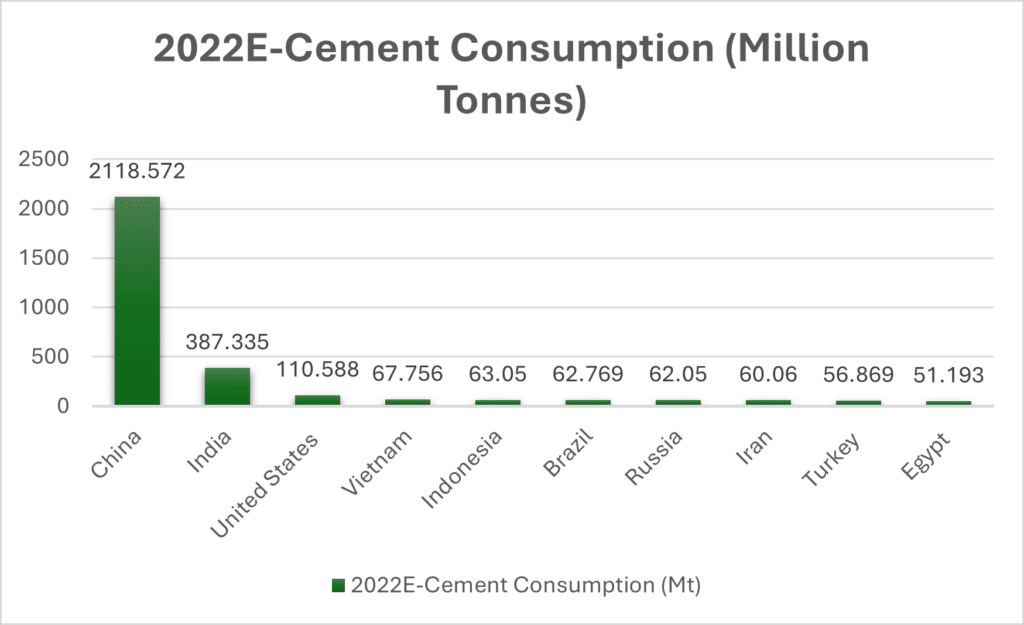
Cement consumption is heavily concentrated in specific regions, with China and India leading the global market. China is the largest consumer of cement in the world, a fact that reflects its massive urbanization, rapid industrial growth, and extensive infrastructure development. The scale of cement consumption in China is unparalleled, driven by the construction of megacities, high-speed rail networks, and large-scale public works projects.
China’s cement usage is so substantial that it far surpasses the consumption levels of the second-largest consumer, India, as well as other countries. This significant gap highlights the country’s unique position in the global construction and manufacturing landscape, emphasizing its role as a key driver of global cement demand.
Cement Consumption Per Capita: A Closer Look at Infrastructure Development
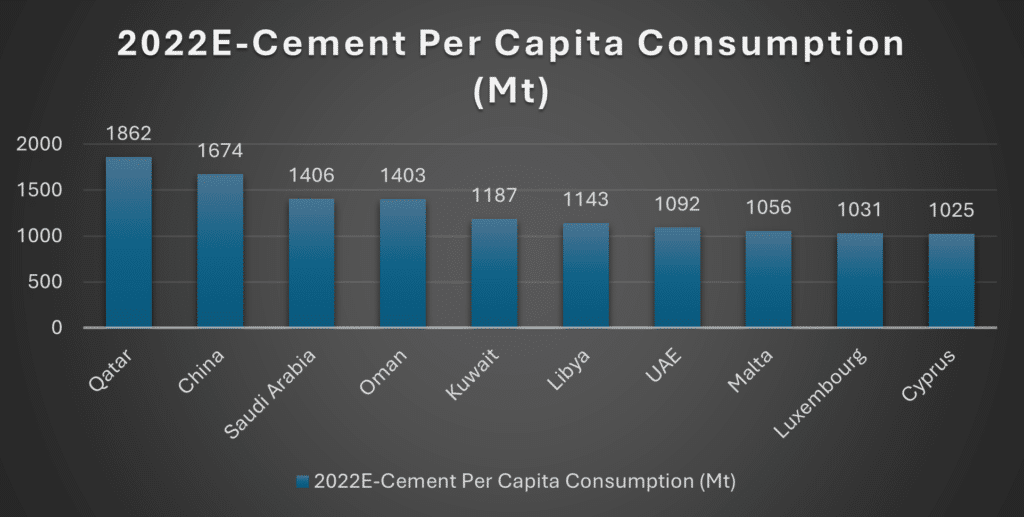
Per capita cement consumption is a key indicator of a country’s real economic growth and development. It is calculated by dividing a nation’s total cement consumption by its population. This metric provides valuable insights into a region’s infrastructure development, urbanization, and construction intensity.
Analysis of global per capita cement consumption reveals that the growth rate is significantly higher in developing economies compared to developed nations. Qatar leads the chart with an impressive 1,862 kilograms per person. This exceptionally high consumption reflects the country’s ambitious infrastructure and development projects, which are remarkable given its relatively small population.
China, the world’s most populous nation, ranks second with a per capita cement consumption of 1,674 kilograms. This figure highlights the country’s extraordinary growth, driven by extensive domestic construction projects and ambitious international ventures. Key initiatives such as the “Belt and Road Initiative” have played a pivotal role in this development, facilitating large-scale infrastructure projects within China and across Asia and Africa.
Conclusion
The past decade of cement production and consumption underscores the dynamic interplay between economic growth, urbanization, and sustainability. Emerging economies continue to drive demand, while global efforts toward sustainable construction are reshaping the industry.
As the world pivots towards green construction practices, the cement industry faces the challenge of balancing growth with environmental responsibility. Adapting to these evolving trends will be critical to meeting global construction needs while minimizing environmental impacts.
This evolving landscape of cement production and consumption reflects the broader challenges and opportunities in today’s world.





